Events & Promotions
|
|

GMAT Club Daily Prep
Thank you for using the timer - this advanced tool can estimate your performance and suggest more practice questions. We have subscribed you to Daily Prep Questions via email.
Customized
for You
Track
Your Progress
Practice
Pays
Not interested in getting valuable practice questions and articles delivered to your email? No problem, unsubscribe here.
- Nov 19
12:30 PM EST
-01:30 PM EST
Learn how Keshav, a Chartered Accountant, scored an impressive 705 on GMAT in just 30 days with GMATWhiz's expert guidance. In this video, he shares preparation tips and strategies that worked for him, including the mock, time management, and more - Nov 18
11:00 AM PST
-12:00 PM PST
Join us in a live GMAT practice session and solve 30 challenging GMAT questions with other test takers in timed conditions, covering GMAT Quant, Data Sufficiency, Data Insights, Reading Comprehension, and Critical Reasoning questions. - Nov 20
01:30 PM EST
-02:30 PM IST
Learn how Kamakshi achieved a GMAT 675 with an impressive 96th %ile in Data Insights. Discover the unique methods and exam strategies that helped her excel in DI along with other sections for a balanced and high score. - Nov 22
11:00 AM IST
-01:00 PM IST
Do RC/MSR passages scare you? e-GMAT is conducting a masterclass to help you learn – Learn effective reading strategies Tackle difficult RC & MSR with confidence Excel in timed test environment - Nov 23
11:00 AM IST
-01:00 PM IST
Attend this free GMAT Algebra Webinar and learn how to master the most challenging Inequalities and Absolute Value problems with ease. - Nov 24
07:00 PM PST
-08:00 PM PST
Full-length FE mock with insightful analytics, weakness diagnosis, and video explanations! - Nov 25
10:00 AM EST
-11:00 AM EST
Prefer video-based learning? The Target Test Prep OnDemand course is a one-of-a-kind video masterclass featuring 400 hours of lecture-style teaching by Scott Woodbury-Stewart, founder of Target Test Prep and one of the most accomplished GMAT instructors.
Kudos
Bookmarks
Question 1
B
Be sure to select an answer first to save it in the Error Log before revealing the correct answer (OA)!
Difficulty:
 5%
(low)
5%
(low)
Question Stats:
90% (02:48) correct 10%
(03:07) wrong
10%
(03:07) wrong  based on 98
sessions
based on 98
sessions
History
Date
Time
Result
Not Attempted Yet
Question 2
D
Be sure to select an answer first to save it in the Error Log before revealing the correct answer (OA)!
Difficulty:
 55%
(hard)
55%
(hard)
Question Stats:
59% (01:31) correct 41%
(01:29) wrong
41%
(01:29) wrong  based on 101
sessions
based on 101
sessions
History
Date
Time
Result
Not Attempted Yet
Question 3
A
Be sure to select an answer first to save it in the Error Log before revealing the correct answer (OA)!
Difficulty:
 15%
(low)
15%
(low)
Question Stats:
83% (00:59) correct 17%
(01:15) wrong
17%
(01:15) wrong  based on 103
sessions
based on 103
sessions
History
Date
Time
Result
Not Attempted Yet
Question 4
E
Be sure to select an answer first to save it in the Error Log before revealing the correct answer (OA)!
Difficulty:
 35%
(medium)
35%
(medium)
Question Stats:
66% (01:12) correct 34%
(01:35) wrong
34%
(01:35) wrong  based on 101
sessions
based on 101
sessions
History
Date
Time
Result
Not Attempted Yet
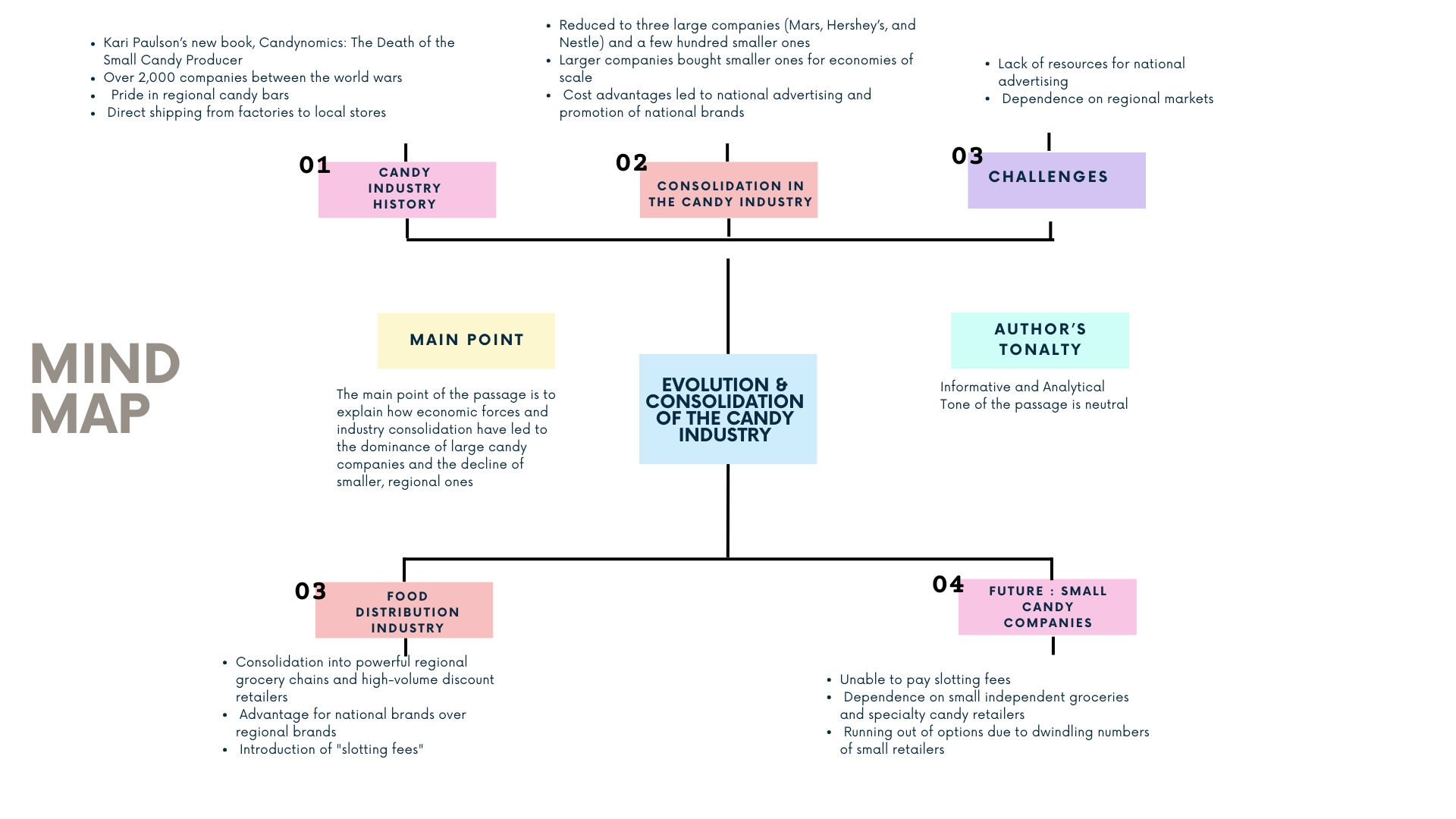
Candy bars may seem sweet to the average consumer, but the companies that make them have to be tougher than nails in order to survive. That, at least, is one of the lessons taken from Kari Paulson’s new book, Candynomics: The Death of the Small Candy Producer. According to Paulson, there were over 2,000 candy companies thriving in the United States in the period between the world wars. Local consumers took pride in their regional candy bars, such as the Caravelle, Clark Bar, Goo Goo Cluster, and the Valomilk, and many factories shipped their confections directly from the factory to local stores. But the economic forces at work over the last sixty years have led to substantial consolidation in the candy industry and, perhaps more importantly, in the way that candy is distributed.
The process that consolidated over 2,000 independent enterprises into three large companies—Mars, Hershey’s, and Nestle—and a few hundred lingering hangers-on has been paralleled in most consumer-oriented manufacturing businesses over the past half century. The largest companies bought up smaller companies in order to grow larger and take advantage of economies of scale in production and distribution. The larger companies could negotiate better rates on sugar, cocoa butter, peanut butter, coconut, and the other central ingredients of the candy industry. These cost advantages resulted in the biggest companies having the financial resources to advertise nationally and to promote national brands such as Snickers, Three Musketeers, and the Mars Bar. The smaller companies, lacking the resources to advertise nationally, stuck to their regional markets.
The strategy of sticking to a regional market, however, only works when there are regional distributors who play along. The consolidation of the food distribution industry over the last few decades into a relatively small number of powerful regional grocery chains and convenience stores, and particularly the overwhelming force now exerted on the entire retail business by extremely high-volume discount retailers such as Walmart and Kmart, has provided a strong advantage for national brands over regional brands. Almost all large food retailers now charge “slotting fees” a payment, often as much as $25,000, to get a particular kind of candy placed on the store shelves. The smaller candy companies, unable to pay the slotting fees demanded by large chains, are relying increasingly on small independent groceries and specialty candy retailers to sell their products. With the numbers of these small retailers dwindling, the smallest candy makers are running out of options.
The process that consolidated over 2,000 independent enterprises into three large companies—Mars, Hershey’s, and Nestle—and a few hundred lingering hangers-on has been paralleled in most consumer-oriented manufacturing businesses over the past half century. The largest companies bought up smaller companies in order to grow larger and take advantage of economies of scale in production and distribution. The larger companies could negotiate better rates on sugar, cocoa butter, peanut butter, coconut, and the other central ingredients of the candy industry. These cost advantages resulted in the biggest companies having the financial resources to advertise nationally and to promote national brands such as Snickers, Three Musketeers, and the Mars Bar. The smaller companies, lacking the resources to advertise nationally, stuck to their regional markets.
The strategy of sticking to a regional market, however, only works when there are regional distributors who play along. The consolidation of the food distribution industry over the last few decades into a relatively small number of powerful regional grocery chains and convenience stores, and particularly the overwhelming force now exerted on the entire retail business by extremely high-volume discount retailers such as Walmart and Kmart, has provided a strong advantage for national brands over regional brands. Almost all large food retailers now charge “slotting fees” a payment, often as much as $25,000, to get a particular kind of candy placed on the store shelves. The smaller candy companies, unable to pay the slotting fees demanded by large chains, are relying increasingly on small independent groceries and specialty candy retailers to sell their products. With the numbers of these small retailers dwindling, the smallest candy makers are running out of options.
1. According to the information given in the passage, which of the following candy bars is most likely to be found in a large regional grocery chain?
A. Caravelle
B. Three Musketeers
C. Charleston Chew
D. Clark Bar
E. Goo Goo Cluster
A. Caravelle
B. Three Musketeers
C. Charleston Chew
D. Clark Bar
E. Goo Goo Cluster
2. Which of the following business examples most closely parallels that of the candy industry in recent decades, as described in the passage?
A. Many formerly non-profit hospitals are bought and managed by large, for-profit health care consortiums that use their size to negotiate better rates from insurance companies and health care product suppliers.
B. A small number of very large agricultural companies purchase hundreds of thousands of acres of farmland from small farmers when a period of sustained drought makes most of these smaller farms nonviable as independent operations.
C. An online book retailer eats into the market share of both large and small traditional book retailers by opening up an entirely new bookbuying marketplace and offering free shipping.
D. A small number of soft-drink conglomerates buy up smaller regional competitors and use economies of scale to negotiate preferential rates from both suppliers and distributors.
E. A medium-sized regional telecom company uses an inflated stock price to purchase a string of smaller regional competitors and in the process becomes one of the largest companies in the telecom industry.
A. Many formerly non-profit hospitals are bought and managed by large, for-profit health care consortiums that use their size to negotiate better rates from insurance companies and health care product suppliers.
B. A small number of very large agricultural companies purchase hundreds of thousands of acres of farmland from small farmers when a period of sustained drought makes most of these smaller farms nonviable as independent operations.
C. An online book retailer eats into the market share of both large and small traditional book retailers by opening up an entirely new bookbuying marketplace and offering free shipping.
D. A small number of soft-drink conglomerates buy up smaller regional competitors and use economies of scale to negotiate preferential rates from both suppliers and distributors.
E. A medium-sized regional telecom company uses an inflated stock price to purchase a string of smaller regional competitors and in the process becomes one of the largest companies in the telecom industry.
3. According to the information presented in the passage, which of the following presents an accurate statement about small and large candy companies?
A. A large candy company can expect to pay less for a given amount of cocoa butter than a small candy company.
B. A small candy company can expect to pay a larger slotting fee for a given space in a retail outlet than a larger company.
C. A small candy company may have one or two national brands, while a large candy company will usually have dozens of regional brands.
D. A large candy company has probably been in operation longer than a small candy company.
E. A small candy company probably offers its employees better employment benefits than does a large candy company.
A. A large candy company can expect to pay less for a given amount of cocoa butter than a small candy company.
B. A small candy company can expect to pay a larger slotting fee for a given space in a retail outlet than a larger company.
C. A small candy company may have one or two national brands, while a large candy company will usually have dozens of regional brands.
D. A large candy company has probably been in operation longer than a small candy company.
E. A small candy company probably offers its employees better employment benefits than does a large candy company.
4. The final sentence of the first paragraph plays what role in the passage?
A. It refutes the conclusions of the first paragraph.
B. It suggests the subject matter for the second paragraph.
C. It raises a question that is answered in the following paragraphs.
D. It suggests an alternative hypothesis to that proposed by Paulson in her book.
E. It provides a conclusion to the premises of the first paragraph and outlines the subject matter of the following paragraphs.
A. It refutes the conclusions of the first paragraph.
B. It suggests the subject matter for the second paragraph.
C. It raises a question that is answered in the following paragraphs.
D. It suggests an alternative hypothesis to that proposed by Paulson in her book.
E. It provides a conclusion to the premises of the first paragraph and outlines the subject matter of the following paragraphs.
GMAT Club's Reading Comprehension (RC) Quiz-II 2023
05 Days | 10 Passages | Win Prizes | Get Better at GMAT
Passage # 04 | Date: 02 September 2023
Click here for more details and master thread
05 Days | 10 Passages | Win Prizes | Get Better at GMAT
Passage # 04 | Date: 02 September 2023
Click here for more details and master thread
Kudos
Bookmarks
1. According to the information given in the passage, which of the following candy bars is most likely to be found in a large regional grocery chain?
The passage mentions Caravelle as a regional candy bar. It doesn't specify the producer, but it implies that such regional bars are less likely to be found in large regional grocery chains due to the consolidation of the candy industry and the high slotting fees.
B. Three Musketeers
The passage mentions that larger companies like Mars, Hershey’s and Nestle have an advantage in large regional grocery chains. Three Musketeers is a product of Mars, which is one of the three large companies mentioned
This candy bar is not mentioned in the passage
Like Caravelle, Clark Bar is mentioned as a regional candy bar in the passage. Same reasoning as A
This is another regional candy bar mentioned in the passage. Same reasoning as A
--
2. Which of the following business examples most closely parallels that of the candy industry in recent decades, as described in the passage?
This option does show consolidation and negotiation of better rates. However, it does not mention the aspect of buying up smaller entities to grow larger which is a key point in the passage about the candy industry.
This option shows consolidation but the reason for the consolidation (a period of drought) is not parallel to the candy industry's situation. The candy industry's consolidation was driven by a desire for economies of scale and better negotiation power, not external environmental factors. We can keep this on hold until there is something better
This option is not parallel, it talks about a new player disrupting the market not consolidation within the industry.
D. A small number of soft-drink conglomerates buy up smaller regional competitors and use economies of scale to negotiate preferential rates from both suppliers and distributors.
This option is better than B and close to the candy industry's consolidation into a few large companies that bought up smaller ones to take advantage of economies of scale in production and distribution. These larger companies could negotiate better rates from suppliers, similar to the soft-drink conglomerates in this option
This option does show a company growing larger by buying up smaller competitors but it does not mention economies of scale or better negotiation power with suppliers, as in D - making D the bigger answer
--
3. According to the information presented in the passage, which of the following presents an accurate statement about small and large candy companies?
A. A large candy company can expect to pay less for a given amount of cocoa butter than a small candy company.
The passage mentions that larger companies could negotiate better rates on ingredients like cocoa butter due to their size and economies of scale.
Passage mentions that slotting fees are a challenge for smaller companies but it doesn't say that these fees are higher for smaller companies than for larger ones.
This is contradictory to the information in the passage. The passage suggests that smaller companies stick to their regional markets, while larger companies promote national brands.
Passage discusses the consolidation of the candy industry and the challenges faced by smaller companies but it doesn't mention how long companies of different sizes have been in operation.
Passage does not discuss employee benefits at candy companies of any size.
--
4. The final sentence of the first paragraph plays what role in the passage?
The final sentence doesn't refute anything, it rather concludes the first paragraph and introduces the subject of the following paragraphs.
The final sentence doesn't raise a question, it states a fact about the consolidation in the candy industry.
The final sentence doesn't propose an alternative hypothesis, it continues the narrative started by Paulson's book.
E. It provides a conclusion to the premises of the first paragraph and outlines the subject matter of the following paragraphs.
This is better than B. The final sentence concludes the first paragraph and outlines the subject matter for the rest of the passage.
Attachment:
File comment: Mind Map of the Candy Industry Passage
Candy Industry.png [ 204.39 KiB | Viewed 3503 times ]
Candy Industry.png [ 204.39 KiB | Viewed 3503 times ]
Kudos
Bookmarks
Para 1: Description of one lesson from KP's new book. Candy companies need to be tougher to survive. Economic forces led Consolidation in candy industry and the way it is distributed. Once this industry was thriving and locals used to take pride in regional candy
Para 2: Process that led consolidation of candy industry is similar to that in manufacturing in past half century. Explains the process . Smaller companies stuck to their regional markets
Para 3: Strategy of sticking to regional market works when distributors play along. Explains why it is being difficult to smaller players and they are running out of options
1. According to the information given in the passage, which of the following candy bars is most likely to be found in a large regional grocery chain?
"These cost advantages resulted in the biggest companies having the financial resources to advertise nationally and to promote national brands such as Snickers, Three Musketeers, and the Mars Bar."
" Local consumers took pride in their regional candy bars, such as the Caravelle, Clark Bar, Goo Goo Cluster, and the Valomilk, "
Almost all large grocery chains charge “slotting fees” a payment, often as much as $25,000, to get a particular kind of candy placed on the store shelves. The smaller candy companies, unable to pay the slotting fees demanded by large chains. So answer should be a product of a large national company
A. Caravelle -- Regional product
B. Three Musketeers -- Product of large national company and is the answer
C. Charleston Chew -- Not mentioned
D. Clark Bar -- Regional product
E. Goo Goo Cluster -- Regional product
2. Which of the following business examples most closely parallels that of the candy industry in recent decades, as described in the passage?
A. Many formerly non-profit hospitals are bought and managed by large, for-profit health care consortiums that use their size to negotiate better rates from insurance companies and health care product suppliers.
-- non-profit hospitals are bought by for profit large consortiums. So though the option looks good, it talks about two different segments and hence out
B. A small number of very large agricultural companies purchase hundreds of thousands of acres of farmland from small farmers when a period of sustained drought makes most of these smaller farms nonviable as independent operations.
-- large agriculture companies are buying farms but there is no small agriculture companies which get diminished from this action. So the option is not in the same line as in example of candy industry
C. An online book retailer eats into the market share of both large and small traditional book retailers by opening up an entirely new bookbuying marketplace and offering free shipping.
--It talks about a new type of retailer that eats both large and small so not in the same line as in candy industry example
D. A small number of soft-drink conglomerates buy up smaller regional competitors and use economies of scale to negotiate preferential rates from both suppliers and distributors.
-- It is in line with what large companies in candy industry did. "The largest companies bought up smaller companies in order to grow larger and take advantage of economies of scale in production and distribution. "
This is the answer
E. A medium-sized regional telecom company uses an inflated stock price to purchase a string of smaller regional competitors and in the process becomes one of the largest companies in the telecom industry.
-- This option shows that medium size firm utilizes foul practises to purchase regional competitors to become one of the largest. While consolidation in candy industry happened and it preferred large companies as they were able to negotiate better
3. According to the information presented in the passage, which of the following presents an accurate statement about small and large candy companies?
"The larger companies could negotiate better rates on sugar, cocoa butter, peanut butter, coconut, and the other central ingredients of the candy industry. These cost advantages resulted in the biggest companies having the financial resources to advertise nationally and to promote national brands"
A. A large candy company can expect to pay less for a given amount of cocoa butter than a small candy company.
-- As a large company could negotiate better rates, they can expect to pay less
This is the answer
B. A small candy company can expect to pay a larger slotting fee for a given space in a retail outlet than a larger company.
-- Does not support as small candy company cannot pay hefty amounts ."Almost all large food retailers now charge “slotting fees” a payment, often as much as $25,000, to get a particular kind of candy placed on the store shelves. The smaller candy companies, unable to pay the slotting fees demanded by large chains, are relying increasingly on small independent groceries"
C. A small candy company may have one or two national brands, while a large candy company will usually have dozens of regional brands.
-- Not given int he passage
D. A large candy company has probably been in operation longer than a small candy company.
-- Not mentioned that large candy company is longer in the operation than small candy company
E. A small candy company probably offers its employees better employment benefits than does a large candy company.
-- Employment benefits are not discussed.
4. The final sentence of the first paragraph plays what role in the passage?
"But the economic forces at work over the last sixty years have led to substantial consolidation in the candy industry and, perhaps more importantly, in the way that candy is distributed."
A. It refutes the conclusions of the first paragraph.
-- It does not refute any conclusion of first paragraph rather concludes the first paragraph and provides context for following paragraphs
B. It suggests the subject matter for the second paragraph.
-- It does suggest subject matter for second paragraph but it also concludes on the what is the lesson from Paulson's new book.
C. It raises a question that is answered in the following paragraphs.
-- it does not raise any question rather explains conclusion of one of the lesson from Paulson's new book.
D. It suggests an alternative hypothesis to that proposed by Paulson in her book.
-- It does not provide any alternate hypothesis of Paulson's new book. infact his book is "Candynomics: The Death of the Small Candy Producer." and the last sentence just elaborates on that rather suggest any alternate hypothesis
E. It provides a conclusion to the premises of the first paragraph and outlines the subject matter of the following paragraphs.[/box_in][/box_out][/align]
-- It does provide a context to the new book, demise of small candy producer and also outlines subject matter for following paragraph
This is the answer
Para 2: Process that led consolidation of candy industry is similar to that in manufacturing in past half century. Explains the process . Smaller companies stuck to their regional markets
Para 3: Strategy of sticking to regional market works when distributors play along. Explains why it is being difficult to smaller players and they are running out of options
1. According to the information given in the passage, which of the following candy bars is most likely to be found in a large regional grocery chain?
"These cost advantages resulted in the biggest companies having the financial resources to advertise nationally and to promote national brands such as Snickers, Three Musketeers, and the Mars Bar."
" Local consumers took pride in their regional candy bars, such as the Caravelle, Clark Bar, Goo Goo Cluster, and the Valomilk, "
Almost all large grocery chains charge “slotting fees” a payment, often as much as $25,000, to get a particular kind of candy placed on the store shelves. The smaller candy companies, unable to pay the slotting fees demanded by large chains. So answer should be a product of a large national company
A. Caravelle -- Regional product
B. Three Musketeers -- Product of large national company and is the answer
C. Charleston Chew -- Not mentioned
D. Clark Bar -- Regional product
E. Goo Goo Cluster -- Regional product
2. Which of the following business examples most closely parallels that of the candy industry in recent decades, as described in the passage?
A. Many formerly non-profit hospitals are bought and managed by large, for-profit health care consortiums that use their size to negotiate better rates from insurance companies and health care product suppliers.
-- non-profit hospitals are bought by for profit large consortiums. So though the option looks good, it talks about two different segments and hence out
B. A small number of very large agricultural companies purchase hundreds of thousands of acres of farmland from small farmers when a period of sustained drought makes most of these smaller farms nonviable as independent operations.
-- large agriculture companies are buying farms but there is no small agriculture companies which get diminished from this action. So the option is not in the same line as in example of candy industry
C. An online book retailer eats into the market share of both large and small traditional book retailers by opening up an entirely new bookbuying marketplace and offering free shipping.
--It talks about a new type of retailer that eats both large and small so not in the same line as in candy industry example
D. A small number of soft-drink conglomerates buy up smaller regional competitors and use economies of scale to negotiate preferential rates from both suppliers and distributors.
-- It is in line with what large companies in candy industry did. "The largest companies bought up smaller companies in order to grow larger and take advantage of economies of scale in production and distribution. "
This is the answer
E. A medium-sized regional telecom company uses an inflated stock price to purchase a string of smaller regional competitors and in the process becomes one of the largest companies in the telecom industry.
-- This option shows that medium size firm utilizes foul practises to purchase regional competitors to become one of the largest. While consolidation in candy industry happened and it preferred large companies as they were able to negotiate better
3. According to the information presented in the passage, which of the following presents an accurate statement about small and large candy companies?
"The larger companies could negotiate better rates on sugar, cocoa butter, peanut butter, coconut, and the other central ingredients of the candy industry. These cost advantages resulted in the biggest companies having the financial resources to advertise nationally and to promote national brands"
A. A large candy company can expect to pay less for a given amount of cocoa butter than a small candy company.
-- As a large company could negotiate better rates, they can expect to pay less
This is the answer
B. A small candy company can expect to pay a larger slotting fee for a given space in a retail outlet than a larger company.
-- Does not support as small candy company cannot pay hefty amounts ."Almost all large food retailers now charge “slotting fees” a payment, often as much as $25,000, to get a particular kind of candy placed on the store shelves. The smaller candy companies, unable to pay the slotting fees demanded by large chains, are relying increasingly on small independent groceries"
C. A small candy company may have one or two national brands, while a large candy company will usually have dozens of regional brands.
-- Not given int he passage
D. A large candy company has probably been in operation longer than a small candy company.
-- Not mentioned that large candy company is longer in the operation than small candy company
E. A small candy company probably offers its employees better employment benefits than does a large candy company.
-- Employment benefits are not discussed.
4. The final sentence of the first paragraph plays what role in the passage?
"But the economic forces at work over the last sixty years have led to substantial consolidation in the candy industry and, perhaps more importantly, in the way that candy is distributed."
A. It refutes the conclusions of the first paragraph.
-- It does not refute any conclusion of first paragraph rather concludes the first paragraph and provides context for following paragraphs
B. It suggests the subject matter for the second paragraph.
-- It does suggest subject matter for second paragraph but it also concludes on the what is the lesson from Paulson's new book.
C. It raises a question that is answered in the following paragraphs.
-- it does not raise any question rather explains conclusion of one of the lesson from Paulson's new book.
D. It suggests an alternative hypothesis to that proposed by Paulson in her book.
-- It does not provide any alternate hypothesis of Paulson's new book. infact his book is "Candynomics: The Death of the Small Candy Producer." and the last sentence just elaborates on that rather suggest any alternate hypothesis
E. It provides a conclusion to the premises of the first paragraph and outlines the subject matter of the following paragraphs.[/box_in][/box_out][/align]
-- It does provide a context to the new book, demise of small candy producer and also outlines subject matter for following paragraph
This is the answer

















