|
|

GMAT Club Daily Prep
Thank you for using the timer - this advanced tool can estimate your performance and suggest more practice questions. We have subscribed you to Daily Prep Questions via email.
Customized
for You
Track
Your Progress
Practice
Pays
Not interested in getting valuable practice questions and articles delivered to your email? No problem, unsubscribe here.
Kudos
Bookmarks
Dropdown 1: 0.018
Dropdown 2: increased approximately by 0.002
Be sure to select an answer first to save it in the Error Log before revealing the correct answer (OA)!
Difficulty:
 95%
(hard)
95%
(hard)
Question Stats:
21% (02:12) correct 79%
(02:13)
wrong
79%
(02:13)
wrong  based on 66
sessions
based on 66
sessions
History
Date
Time
Result
Not Attempted Yet
Lenses used in outer space video recording devices obviously require superior optical, thermal and barometric characteristics. In 2011, researchers at NASA synthesized a polymer, X21F702089 (Optical density = 0.02, Spectral absorption = 0.012) which is currently being used in all the recording equipment in their Curiosity space shuttle. Although the polymer performs flawlessly on Earth and in space (its optical density and spectral absorption remain constant), recent images of Mars captured by Curiosity suggest that, on Mars, X21F702Q89 has not been functioning the way it was supposed to This led to a battery of tests being conducted on X21F702089 in simulated Mars-like conditions. The research team for these experiments is led by Dr. Sy Fields, a nobel-prize winning Materials Science engineer. The tests continued until the polymer reached its maximum optical density. This is a portion of a graph (submitted by Dr. Fields' team) showing the variation of optical density and spectral density of X21F702089 with time spent in a Mars-like environment.
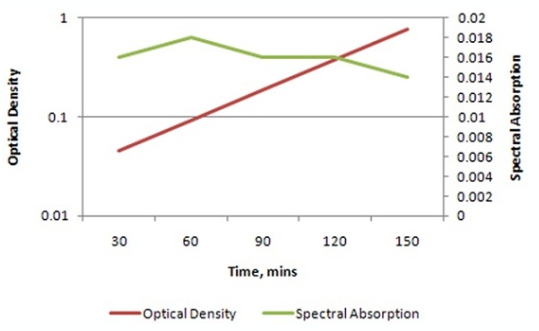
From each drop-down menu, select the option that creates the most accurate statement based on the information provided in the graph
A. When the optical density of X21F702089 becomes 0.1, its spectral distribution is at approximately
B. When X21F702089 attains maximum optical density, its spectral distribution since its entry into Mars-like environment.

GMAT-Club-Forum-tt109fuy.png [ 109.32 KiB | Viewed 227 times ]
From each drop-down menu, select the option that creates the most accurate statement based on the information provided in the graph
A. When the optical density of X21F702089 becomes 0.1, its spectral distribution is at approximately
B. When X21F702089 attains maximum optical density, its spectral distribution since its entry into Mars-like environment.
Attachment:
GMAT-Club-Forum-tt109fuy.png [ 109.32 KiB | Viewed 227 times ]
ShowHide Answer
Official Answer
Dropdown 1: 0.018
Dropdown 2: increased approximately by 0.002






