Events & Promotions
|
|

GMAT Club Daily Prep
Thank you for using the timer - this advanced tool can estimate your performance and suggest more practice questions. We have subscribed you to Daily Prep Questions via email.
Customized
for You
Track
Your Progress
Practice
Pays
Not interested in getting valuable practice questions and articles delivered to your email? No problem, unsubscribe here.
- Nov 20
07:30 AM PST
-08:30 AM PST
Learn what truly sets the UC Riverside MBA apart and how it helps in your professional growth - Nov 20
01:30 PM EST
-02:30 PM IST
Learn how Kamakshi achieved a GMAT 675 with an impressive 96th %ile in Data Insights. Discover the unique methods and exam strategies that helped her excel in DI along with other sections for a balanced and high score. - Nov 22
06:30 AM PST
-08:30 AM PST
Let’s dive deep into advanced CR to ace GMAT Focus! Join this webinar to unlock the secrets to conquering Boldface and Paradox questions with expert insights and strategies. Elevate your skills and boost your GMAT Verbal Score now! - Nov 22
11:00 AM IST
-01:00 PM IST
Do RC/MSR passages scare you? e-GMAT is conducting a masterclass to help you learn – Learn effective reading strategies Tackle difficult RC & MSR with confidence Excel in timed test environment - Nov 23
11:00 AM IST
-01:00 PM IST
Attend this free GMAT Algebra Webinar and learn how to master the most challenging Inequalities and Absolute Value problems with ease. - Nov 24
07:00 PM PST
-08:00 PM PST
Full-length FE mock with insightful analytics, weakness diagnosis, and video explanations! - Nov 25
10:00 AM EST
-11:00 AM EST
Prefer video-based learning? The Target Test Prep OnDemand course is a one-of-a-kind video masterclass featuring 400 hours of lecture-style teaching by Scott Woodbury-Stewart, founder of Target Test Prep and one of the most accomplished GMAT instructors.
Kudos
Bookmarks
Dropdown 1: is a decrease of about 60%
Dropdown 2: 16
Be sure to select an answer first to save it in the Error Log before revealing the correct answer (OA)!
Difficulty:
 55%
(hard)
55%
(hard)
Question Stats:
64% (02:55) correct 36%
(02:58)
wrong
36%
(02:58)
wrong  based on 3122
sessions
based on 3122
sessions
History
Date
Time
Result
Not Attempted Yet
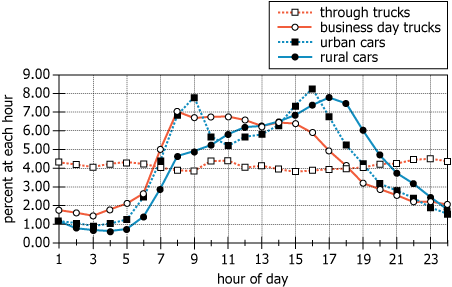
The traffic that passes through a certain location is composed exclusively of the following nonoverlapping types of vehicles: “rural cars,” “urban cars,” “business day trucks,” and “through trucks.” For each of these vehicle types, and for each hour of the day, the graph depicts the typical percentage of the total number of the given type of vehicle passing through the location during that hour. For example, the graph indicates that slightly less than 8 percent of all urban cars that pass through the location on a typical day do so during hour 9.
On the basis of the given information, select from each of the drop-down menus the option that makes the statement most accurate.
From hour 17 to hour 22, the percent change in number of business day trucks passing through the location .
Assuming that total traffic over the day is the same for each of the four vehicle types, the hour of maximum total traffic is .

The traffic that passes through a certain location is composed exclusively of the following nonoverlapping types of vehicles: “rural cars,” “urban cars,” “business day trucks,” and “through trucks.” For each of these vehicle types, and for each hour of the day, the graph depicts the typical percentage of the total number of the given type of vehicle passing through the location during that hour. For example, the graph indicates that slightly less than 8 percent of all urban cars that pass through the location on a typical day do so during hour 9.
On the basis of the given information, select from each of the drop-down menus the option that makes the statement most accurate.
From hour 17 to hour 22, the percent change in number of business day trucks passing through the location .
Assuming that total traffic over the day is the same for each of the four vehicle types, the hour of maximum total traffic is .
ID: 100352
ShowHide Answer
Official Answer
Dropdown 1: is a decrease of about 60%
Dropdown 2: 16
Kudos
Bookmarks
guddo
What we should know: The sum of all the points on each of the line should add up to 100. For example, tak ethe case of through trucks, the dotted orange lines. All 24 points are close to 4%, so they will add up to something greater than 24*4 or 96%.
1. From hour 17 to hour 22, the percent change in number of business day trucks passing through the location
Since the % on each line has the same base, the number of business day trucks, say b in total, will result in
At hour 17: 5%, so \(\frac{5}{100}*b = 0.05*b\)
At hour 22: 2.1%, so \(\frac{2.1}{100}*b = 0.021*b\)
Change = (0.05 - 0.021)b ~ 0.03b
% change = \(\frac{0.03b}{0.05b}*100=\frac{3}{5}*100\) = 60
2. Assuming that total traffic over the day is the same for each of the four vehicle types, the hour of maximum total traffic is
So, 100% of each is equal, meaning each of the % refers to same total quantity.
We should just check for the options given.
Hour 9: (4+5+6.8+7.8)% = 23.6%
Hour 15: (3.9+6.4+6.8+7.2)% = 24.3%
Hour 16: (4+6+7.3+8.1)% = 25.4%
Kudos
Bookmarks
A) the percent change in the number of business-day trucks passing through the location from hour 17 to hour 22
Day 17 = 5%, Day 22 = approx 2.1%
%Change (from 17 to 22)= [(2.1-5)/5]*100 = 60%
B. Assuming that total traffic over the day is the same for each of the four vehicle types, the hour of maximum total traffic is?
We have options 9, 15, and 16. We can either add all the hours from the graphs for these options or compare the difference in the percentage change for these different hours. Both ways will give us 16 hr as answer.
Day 17 = 5%, Day 22 = approx 2.1%
%Change (from 17 to 22)= [(2.1-5)/5]*100 = 60%
B. Assuming that total traffic over the day is the same for each of the four vehicle types, the hour of maximum total traffic is?
We have options 9, 15, and 16. We can either add all the hours from the graphs for these options or compare the difference in the percentage change for these different hours. Both ways will give us 16 hr as answer.















